Buzzer/en: различия между версиями
(Новая страница: «[https://github.com/contactless/wirenboard/tree/master/examples/beeper '''Example''']») |
Matveevrj (обсуждение | вклад) (Новая страница: «==Management from web interface==») |
||
| Строка 1: | Строка 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Зуммер (звуковой излучатель)}} | |||
<languages/> | <languages/> | ||
The sound emitter is | ==Description== | ||
The Wiren Board controller has a Buzzer (sound emitter) on board. The buzzer is powered by 5V and controlled by the CPU's gpio pin in PWM mode. The buzzer can be controlled through the sysfs interface of the kernel and various software on top of it. Management from the web interface, the wb-rules rule engine and python is now implemented. | |||
==Management from web interface== | |||
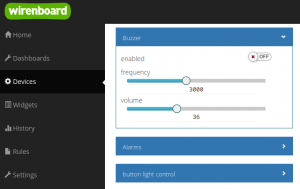
[[File:buzzer.png |300px|thumb|right| Buzzer control]] | |||
In the web interface of the controller, buzzer control is available in the ''"Devices"'' tab. Parameter ''"Frequency"'' - sound frequency in Hz. ''"Volume"'' - volume (in conventional units, linear scale). The settings are saved when the controller is rebooted. | |||
==Control from rule engine== | |||
The buzzer control displayed in the web interface is a virtual device created by the wb-rules system rule when the controller starts. The source code of the rule is available [https://github.com/wirenboard/wb-rules-system/blob/master/rules/buzzer.js on our github]. | |||
You can learn more about what virtual devices are for in the [[wb-rules|description of the rules engine]]. | |||
The system rule internally implements tone and volume recalculation (see [[#About PWM and parameter recalculation|section on recalculation]]) and work with pwm via sysfs (see [[#Working from sysfs|corresponding section]]). Outside, the user has access to the ''"buzzer"'' device, which has several mqtt controls: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!Device||Control||Type||Max value||Description | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|Buzzer | |||
|Frequency | |||
|range | |||
|7000 | |||
|Sound frequency | |||
|- | |||
|Volume | |||
|range | |||
|100 | |||
| Volume,% | |||
|- | |||
|Enabled | |||
|Switch | |||
| | |||
|Enable/Disable | |||
|} | |||
Device controls can be used in custom rules. More details about the structure of mqtt topics for virtual and physical devices can be found in our [https://github.com/wirenboard/conventions/blob/main/README.md mqtt convention]. | |||
==Control from python== | |||
On Wiren Board controllers, you can work with the buzzer from python using the ''beeper'' module from the ''wb_common'' package. This is a wrapper around the sysfs interface. The module is preinstalled on all controllers as part of the ''python-wb-common'' deb package. The source code is available [https://github.com/wirenboard/wb-common/blob/master/wb_common/beeper.py on our github]. | |||
Working example from python: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | |||
from wb_common import beeper | |||
beeper.beep(0.5, 2) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
All sysfs interface settings are supported (recalculation must be done manually; see [[#About PWM and parameter recalculation|section on recalculation]]). | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
<br/> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
PWM is a rectangular pulse, the core interface allows you to adjust the pulse rate and fill factor. Coeffecient filling effect on the sound volume. | PWM is a rectangular pulse, the core interface allows you to adjust the pulse rate and fill factor. Coeffecient filling effect on the sound volume. | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
Exporting port to sysfs: | Exporting port to sysfs: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
echo 2 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export | echo 2 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
After that, the /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2 folder appears | After that, the /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2 folder appears | ||
</div> | |||
< | <div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | ||
Sets the period in nanoseconds. The conversion from frequency(from kilohertz per period in nanoseconds is produced by the formula: | Sets the period in nanoseconds. The conversion from frequency(from kilohertz per period in nanoseconds is produced by the formula: | ||
<b> | <b> | ||
T(ns) = 1 000 000 / f(kHz) | T(ns) = 1 000 000 / f(kHz) | ||
</b> | </b> | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
echo 250000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/period # set the period to 250 000 NS, ie 250mks, which corresponds to a frequency of 4kHz | echo 250000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/period # set the period to 250 000 NS, ie 250mks, which corresponds to a frequency of 4kHz | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
Setting the duty_cycle (the duration of the high state) in nanoseconds. Maximum volume is reached at duty_cycle = period / 2 | Setting the duty_cycle (the duration of the high state) in nanoseconds. Maximum volume is reached at duty_cycle = period / 2 | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
echo 125000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/duty_cycle #set duty_cycle to 125 000 NS, i.e. in half of the period | echo 125000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/duty_cycle #set duty_cycle to 125 000 NS, i.e. in half of the period | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
Enable PWM output: | Enable PWM output: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/enable | echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/enable | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
Shutdown: | Shutdown: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
echo 0 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/enable | echo 0 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/enable | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | |||
[https://github.com/contactless/wirenboard/tree/master/examples/beeper '''Example'''] | [https://github.com/contactless/wirenboard/tree/master/examples/beeper '''Example'''] | ||
</div> | |||
Установка периода в наносекундах. Пересчёт из частоты (в килогерцах) в период (в наносекундах) производится по формуле: | |||
<b> | |||
T(ns) = 1 000 000 / f(kHz) | |||
</b> | |||
Версия 20:46, 22 сентября 2022
Description
The Wiren Board controller has a Buzzer (sound emitter) on board. The buzzer is powered by 5V and controlled by the CPU's gpio pin in PWM mode. The buzzer can be controlled through the sysfs interface of the kernel and various software on top of it. Management from the web interface, the wb-rules rule engine and python is now implemented.
Management from web interface
In the web interface of the controller, buzzer control is available in the "Devices" tab. Parameter "Frequency" - sound frequency in Hz. "Volume" - volume (in conventional units, linear scale). The settings are saved when the controller is rebooted.
Control from rule engine
The buzzer control displayed in the web interface is a virtual device created by the wb-rules system rule when the controller starts. The source code of the rule is available on our github.
You can learn more about what virtual devices are for in the description of the rules engine.
The system rule internally implements tone and volume recalculation (see section on recalculation) and work with pwm via sysfs (see corresponding section). Outside, the user has access to the "buzzer" device, which has several mqtt controls:
| Device | Control | Type | Max value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buzzer | Frequency | range | 7000 | Sound frequency |
| Volume | range | 100 | Volume,% | |
| Enabled | Switch | Enable/Disable |
Device controls can be used in custom rules. More details about the structure of mqtt topics for virtual and physical devices can be found in our mqtt convention.
Control from python
On Wiren Board controllers, you can work with the buzzer from python using the beeper module from the wb_common package. This is a wrapper around the sysfs interface. The module is preinstalled on all controllers as part of the python-wb-common deb package. The source code is available on our github.
Working example from python:
from wb_common import beeper
beeper.beep(0.5, 2)
All sysfs interface settings are supported (recalculation must be done manually; see section on recalculation).
PWM is a rectangular pulse, the core interface allows you to adjust the pulse rate and fill factor. Coeffecient filling effect on the sound volume.
Exporting port to sysfs:
echo 2 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export
After that, the /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2 folder appears
Sets the period in nanoseconds. The conversion from frequency(from kilohertz per period in nanoseconds is produced by the formula: T(ns) = 1 000 000 / f(kHz)
echo 250000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/period # set the period to 250 000 NS, ie 250mks, which corresponds to a frequency of 4kHz
Setting the duty_cycle (the duration of the high state) in nanoseconds. Maximum volume is reached at duty_cycle = period / 2
echo 125000 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/duty_cycle #set duty_cycle to 125 000 NS, i.e. in half of the period
Enable PWM output:
echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/enable
Shutdown:
echo 0 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm2/enable
Установка периода в наносекундах. Пересчёт из частоты (в килогерцах) в период (в наносекундах) производится по формуле: T(ns) = 1 000 000 / f(kHz)